Structure A Is A _____.
fonoteka
Sep 17, 2025 · 7 min read
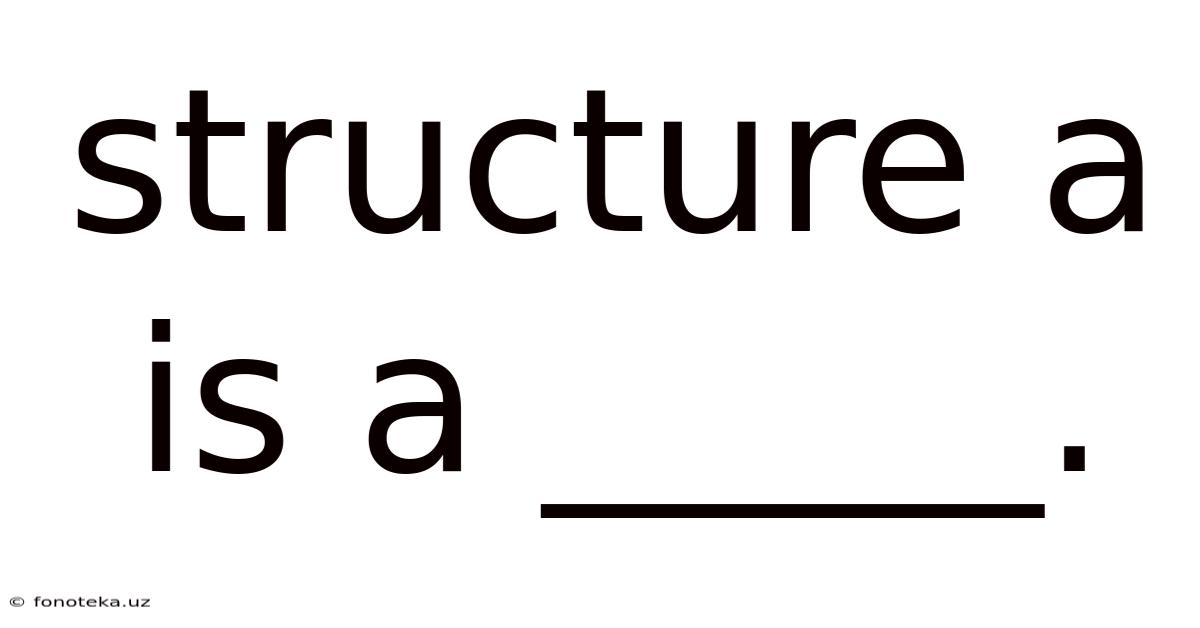
Table of Contents
Structure Is a System: Understanding the Principles of Structural Organization
Understanding "structure" is fundamental to comprehending the world around us. From the intricate workings of a cell to the majestic architecture of a skyscraper, the concept of structure pervades every aspect of our reality. But what exactly is structure? This article delves deep into the multifaceted nature of structure, exploring its underlying principles, examining diverse examples, and highlighting its crucial role across various disciplines. We'll uncover why understanding structural organization is key to solving problems and fostering innovation in fields ranging from engineering to biology.
Introduction: Defining Structure
At its core, structure is a system of interconnected parts that form a unified whole. It's not merely a collection of elements; rather, it’s defined by the relationships and interactions between those elements. This system possesses a specific arrangement and organization, dictated by its function, material properties, and environmental influences. The term "structure" can be applied to both tangible and intangible entities, from the physical structure of a building to the social structure of a community, and even the abstract structure of an argument. The unifying thread is the presence of organized components working together to achieve a specific purpose or exhibit specific properties.
Key Principles of Structural Organization
Several key principles govern the formation and functionality of structures:
- Interdependence: The parts of a structure are interconnected and rely on each other. The failure of one component can compromise the entire system.
- Stability: A well-designed structure resists external forces and maintains its integrity. This involves considerations of balance, strength, and resilience.
- Efficiency: Structures are often optimized for their intended purpose, minimizing material usage while maximizing strength and functionality.
- Adaptation: Structures evolve and adapt to their environment and intended use. This can involve changes in design, material selection, or operational procedures.
- Hierarchy: Many complex structures exhibit a hierarchical organization, with smaller components forming larger sub-systems, which in turn contribute to the overall structure.
Types of Structures: A Diverse Landscape
The concept of "structure" manifests in countless forms across different domains. Let's examine a few key examples:
1. Biological Structures: The Marvels of Nature
Biological structures exemplify the elegance and complexity of organized systems. From the microscopic structures of cells to the macroscopic structures of organisms, biological systems demonstrate remarkable adaptation and efficiency.
- Cellular Structures: Cells are the fundamental building blocks of life. Their internal structure, including organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum, works in concert to maintain cellular function. The intricate arrangement of these components allows for efficient energy production, protein synthesis, and waste removal.
- Organismal Structures: The organization of tissues, organs, and organ systems in multicellular organisms is crucial for their survival. The skeletal system provides support and protection, while the circulatory system transports nutrients and oxygen throughout the body. The precise arrangement of these components ensures the coordinated functioning of the organism as a whole.
- Ecosystem Structures: Even ecosystems exhibit structural organization, with complex interactions between different species and their environment. The food web, for instance, illustrates the interconnectedness of various organisms and their roles in the ecosystem's functioning.
2. Engineering Structures: Human-Made Wonders
Engineering structures represent humanity's ability to design and build complex systems to meet specific needs. These structures often face stringent requirements regarding safety, durability, and efficiency.
- Building Structures: Skyscrapers, bridges, and dams are marvels of engineering, showcasing the principles of structural mechanics. Their design involves careful consideration of material properties, load distribution, and environmental factors to ensure stability and safety.
- Mechanical Structures: Machines, vehicles, and other mechanical systems are composed of intricate structures designed for specific functions. The arrangement of components, such as gears, levers, and linkages, determines the machine's overall performance.
- Civil Engineering Structures: Roads, tunnels, and water management systems are crucial components of infrastructure. Their design involves considerations of soil mechanics, hydrology, and traffic flow to ensure functionality and safety.
3. Social Structures: The Fabric of Society
Social structures refer to the patterns of relationships and interactions within a society. These structures influence how individuals behave and interact, shaping the social landscape.
- Family Structures: Family structures are fundamental units of society, providing social support and shaping individual development. Different cultures have diverse family structures, reflecting variations in social norms and values.
- Organizational Structures: Businesses, governments, and other organizations have internal structures that dictate roles, responsibilities, and communication flows. Effective organizational structures are essential for efficient operation and goal achievement.
- Political Structures: Political systems, including governments and political parties, have structures that define power relationships and decision-making processes. These structures shape political dynamics and influence social policy.
4. Abstract Structures: Concepts and Systems
The concept of structure also applies to abstract systems and concepts. These structures may not be physically tangible, but they possess organization and relationships that contribute to their overall function.
- Data Structures: In computer science, data structures are ways of organizing and storing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently. Different data structures, such as arrays, linked lists, and trees, have different properties and are suited to different tasks.
- Linguistic Structures: Languages have intricate grammatical structures that dictate sentence formation and meaning. The rules of grammar define the relationships between words and phrases, enabling communication.
- Argumentative Structures: Effective arguments possess a logical structure, with a clear thesis statement, supporting evidence, and a conclusion. This organization ensures that the argument is coherent and persuasive.
The Importance of Understanding Structure
Comprehending the principles of structural organization is crucial for several reasons:
- Problem Solving: Analyzing the structure of a problem can help identify its key components and relationships, leading to more effective solutions.
- Innovation: Understanding existing structures enables the design of improved or novel structures with enhanced functionality and efficiency.
- Predictive Modeling: Analyzing structural organization allows us to predict the behavior of systems under different conditions, leading to improved safety and performance.
- System Optimization: By understanding how the components of a structure interact, we can optimize its performance and efficiency.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: The concept of structure is universal, facilitating collaboration across diverse fields.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between structure and function?
A: Structure refers to the arrangement and organization of components, while function refers to the purpose or activity of a system. Structure and function are intimately related; the structure of a system often dictates its function, and the required function often dictates the optimal structure.
Q: Can structures be changed or modified?
A: Yes, structures can be changed or modified, although the extent of modification depends on the nature of the structure and its purpose. Changes can involve alterations to individual components, the overall arrangement, or the materials used.
Q: How does understanding structure help in problem-solving?
A: By breaking down a complex problem into its constituent parts and analyzing their relationships, understanding structure enables a systematic and efficient approach to problem-solving. This allows for targeted interventions and more effective solutions.
Q: Are there limits to the complexity of structures?
A: While the complexity of structures can be immense, there are practical limits to the level of complexity that can be effectively managed and controlled. These limits are determined by factors such as material properties, manufacturing capabilities, and computational resources.
Conclusion: The Enduring Power of Structure
In conclusion, structure is a fundamental concept that underpins our understanding of the world. It's a unifying principle that transcends disciplinary boundaries, connecting the intricacies of biological systems to the grandeur of human-made constructions. By understanding the principles of structural organization, we can unlock a deeper appreciation of the complexity and elegance of the systems around us, fostering innovation and problem-solving across a multitude of fields. The ability to analyze, design, and modify structures is a testament to human ingenuity and our capacity to shape the world around us. From the smallest cell to the largest ecosystem, the study of structure unveils a profound and interconnected tapestry of organization, demonstrating the enduring power of systems working in harmony.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Thel E Refers To The
Sep 17, 2025
-
Congenital Deafness Refers To Deafness
Sep 17, 2025
-
The Word Photography Literally Means
Sep 17, 2025
-
Esthetician State Board Exam Practice
Sep 17, 2025
-
Positions In 6 Man Football
Sep 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Structure A Is A _____. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.